Creating a 3d Printing Revolution.
In the 3D printing process, Layers 3D design and generate the model of an object using the most powerful digital software, and the object is created/printed by the 3D printer by adding layer by layer of material until the shape of the object is completely formed. Additive Manufacturing (AM) is another term for 3D printing.
Full Color Jet Printing
Layers 3D provides Full Color Jet Printing services to our customers. It is one of the latest technology that we added to our 3D printing services. Full colour jet printing is a popular additive manufacturing technique for producing high-quality full-color 3D models. Its printing process is similar to that of an inkjet printer, but instead of paper, it prints on thin layers of white composite powder. The powder will be spread in layers to the building platform, and the ink here is the color binding agent that is deposited by the printer head. The powder is held together by the color binder. Five different colored binders are combined to directly produce the colors of the model while also forming its shape. This procedure is repeated in very thin layers as low as 10 µm until the desired object is formed.
At Layers 3D, this method is commonly used in architectural models, machine models, educational models, and other similar applications. Your models will then go through a premium finishing process to ensure a flawless appearance and protect the material.
One of the most significant advantages of full-color jet printing is the ability to print full-color 3D objects. It is also a cost-effective technology that does not require any support structures because the powder bed gives support and functionality.

Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Layers 3D uses Fused Deposition Modeling, which is also one of the most popular 3D printing processes. The thermoplastic polymers that are used as the building blocks for FDM come in the form of filaments. The procedure begins with the melting of the plastic filament, which is then moved layer by layer across a surface. This layer becomes a solid object. The object will be finished once all of the layers have been completed. FDM converts digital design files into physical dimensions by uploading them to the machine itself.
This technology generates prints that are reasonably durable. If Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is used as the thermoplastic, it can be used in industrial and engineering fields also. Wood, PLA, ABS, PETG, ePA-CF, Nylon, carbon fiber, Flexible TPU, TPE, and other materials are available for FDM printing at Layers 3D. This process has a high degree of accuracy, a low cost, and a wide range of materials selection. It is comparatively faster than other technologies which makes the entire printing process faster.
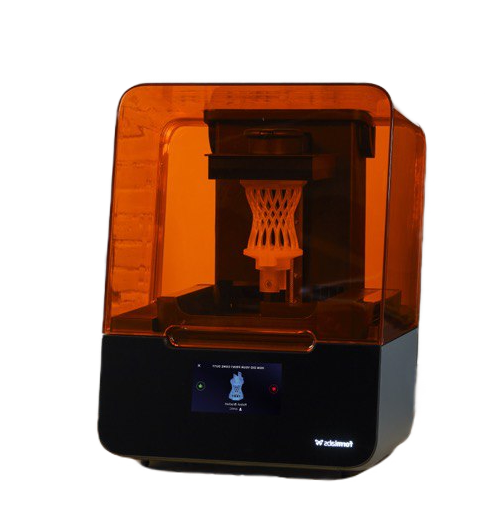
Stereolithography (SLA)
Another 3D printing technique utilized by Layers 3D printing is stereolithography. Light-reactive thermoset materials known as “resin” are used in SLA 3D printers. When SLA resins are exposed to particular light wavelengths, short molecular chains are formed and polymerizing monomers and oligomers take the form of flexible geometries. These polymers then form the body of a three-dimensional model that we designed.
Layers 3D prints 3D models on printers equipped with an 8K Mano screen to achieve the best and greatest results possible. The majority of its applications include jewellery molds and dental models as small as 10 m.
The ability of this process to create high-accuracy prototypes and parts in a wide range of advanced materials with perfect features has made it extremely popular. The speed of SLA is one of its other advantages. Of all 3D printing technologies, SLA modes have the sharpest details and the smoothest surface finishes.


Laser Engraving
Layers 3D uses laser cutting and engraving to produce a wide range of models. The laser engraving technique engraves materials using highly powerful lasers. When a laser removes material from an object’s surface, it leaves behind permanent marks, which is how laser engraving works. When the computer is loaded with the desired design’s data, the laser positions itself in the areas that need to be engraved. And to create the intense heat necessary for vaporization, the laser delivers concentrated amounts of energy to specific locations.
Because laser engraving is so versatile, so many industries rely on it for production. The ability of this process to engrave 2D codes with high readability rates even after post-processing treatments is undoubtedly its most remarkable feature. Layers 3D uses it to engrave and cut non-metallic materials such as wood, paper, leather, acrylic, and so on. The technology is ideal for a variety of applications due to its low cost, increased performance, and good materials.


